| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Portulacaceae |
| Name acc. to: | APGII |
| Herbar: | list records    |
| Description: | herbs |
| open map in a new window | 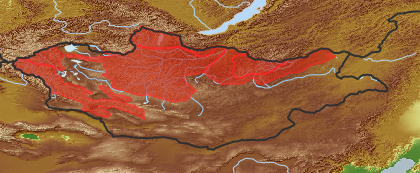 |
| genus: 2 |
| species: 2 |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | herb (i)Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody
example: Artemisia pectinata 
|
| Size of plant: (i)Attention: use flowering or fruiting specimens to assess plant height (many biennial plants possess only a basal rosette in the first year). | from 100 mm to 250 mm
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | terrestrial (i)Plant grows on dry land
example: Orostachys spinosa
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf development: (i)Structure and development of leaves. | with green leaves (i)Plant with green leaves
|
| Leaf arrangement: (i)Arrangement of leaves at the stem. | opposite, opposite-decussate (i)Two leaves per node
example: Lamiaceae, e.g. Phlomis  
|
| Simple or divided leaves: (i)Are the leaves simple or completely divided in several parts? Blade of the leaf entire or (more or less) deeply dissected. Attention: There are various appearances of the leaf margin (from entire to toothed and lobed). Here, we ignore this and ask only for dissections that separate the leaf for more than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. Sometimes, it is difficult to tell apart compound leaves from a shoot system with simple leaves: look for stipulae and/or axillary buds at the ground of the leaves: if only some possess these structures, the others are most likely leaflets of a compound leaf. | simple (i)Non-divided leaf, but margin may be incised nearly to the ground 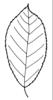
|
| Leaf margin: (i)Structure of leaf margin (or that of a leaflet in case of compound leaves). Attention: Here we ask for the leaf margin, defined as all those dissections that separate the leaf for less than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. To be worked out: how to handle margin of pinnate leaves? | entire (i)Plain margin, not toothed
example: Iris 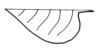
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita 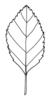  
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants (i)Small, colourless or green flowers
example: Betula, grasslike plants: Carex, Setaria, Juncus
|
| Flower symmetry: (i)Symmetry of the perianth leaves. Attention: to assess this character, look on sepals, petals and stamens, but neglect carpels and ovary. | radiary, regular (actinomorphic) (i)More than two axis of symmetry
example: Saxifraga: 5; Iris: 3 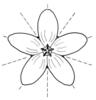
|
| Petal / Tepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the petal leaves connected? Petals sympetalous. | free (i)all petal leaves separate from each other
example: Anthriscus
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum
|
| Stamen fusion: (i)To which degree are the stamens fused? Attention: Whereas the pollen sacs itself are often free., their stalks (filaments) may be fused. Here, we count them as fused if they are together over at least one thirth of their length. | free (i)Stamens with separate bases
example: Malus
|
| Style number: (i)Portion of the pistil connecting the stigma to the ovary. | 3
5
|
| Fruit (i)the seed bearing organ, with or without adnate parts; a ripened ovary and any other structures which are attached and ripen with it. Aggregate fruits are handled like simple fruits for determination. | |
| Consistency: (i)Fleshy fruits or dry fruits, see dispersal adaptations for further classification. | dry (i)With a dry outer shell, no fleshy parts, but seed (embryo) could be edible
|
| Type of fruit: (i)Common fruit types (including pseudocarp). | Solitary fruits (i)  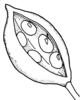 
capsule (i)Dry dehiscent fruit, releasing seeds by slits or holes.
example: Poppy, most Caryophyllaceae, Cerastium, a lot of Scrophulariaceae, Iris (oppened capsule looks like Delphinium), Zygophyllum - it is a very common fruit type 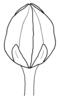  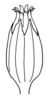
Dehiscent fruits (i)Fruits open along a longitudinale line (except silicula)
|
| Opening of fruit: (i)Mode of dehiscence at maturity to release seeds. | opening / dehiscent (i)Dry? Fruits opening with different types
|
| Shoot/Stem (i)a young stem or branch | |
| Spines, thorns or prickles: (i)Shoot with conspicuous spines, thorns or prickles. | spines or thornes (i)Sharp pointed woody structure originating from the plant (thornes derived from a reduced branch, spines from leaves)
example: Prunus spinosa no in Mongolia
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Caryophyllales: allorhizous inherited by order Caryophyllales: allorhizous
|