| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Alismatales |
| Family: | Araceae |
| Name acc. to: | APGII |
| Synonym: | Acoraceae (acc. to Stace 2010) |
| Description: | Aquatic plants with long Iris-like leaves and rhizome. Small Flowers aggregated in a cylindrical, lateral inflorescence with leaf-like continuation of main axis. |
| Comments: | Plant with Iris-like appearence. Fresh leaves smell spicy. |
| open map in a new window |  |
| genus: 1 |
| species: 1 |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | herb (i)Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody
example: Artemisia pectinata 
|
| Size of plant: (i)Attention: use flowering or fruiting specimens to assess plant height (many biennial plants possess only a basal rosette in the first year). | from 600 mm to 1000 mm
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | water or swamp plant
plants in swamps, marshes or bogs, leaves rising above water (i)Semiaquatic; plant terrestrial, but restricted to wet or moistured environments with ground water at or near the surface
example: Phragmites communis
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf development: (i)Structure and development of leaves. | flattened blade (i)Cross-section of lamina flat, plain
common leaf (i)Green, often divided in blade and petiole
example: Cotoneaster
|
| Leaf arrangement: (i)Arrangement of leaves at the stem. | alternate (i)One leaf per node; distiche: arranged in two vertical rows, equitant
example: Phragmites  
|
| Shape of blade: (i)Easy for simple leaves. In compound leaves use the general shape of leaflet. Always check the ground for largest leaves of a plant. To be worked out: how to handle pinnate leaves? | linear incl.grasslike or oblong (i)Leaves more than two times longer than broad with more or less parallel margins; see character: stipule for ligula
example: Dracocephalum ruyschiana, Poaceae, Scutellaria scordifolia, Pinus 
|
| Length of leaves: (i)How long is the leaf, be carefull in compound leaves, measure the complete leaf. | more than 50 mm
|
| Leaf margin: (i)Structure of leaf margin (or that of a leaflet in case of compound leaves). Attention: Here we ask for the leaf margin, defined as all those dissections that separate the leaf for less than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. To be worked out: how to handle margin of pinnate leaves? | entire (i)Plain margin, not toothed
example: Iris 
|
| Petiole: (i)Leaf divided into stalk (petiole) and blade. | without (i)Leaves without petiole (stalk), sessile
example: Poaceae, Iris 
|
| Stipule: (i)Leaflets at the base of the petiole, these are smaller and of different shape. | none (i)Without stipules
example: Euphorbia, Ericaceae s.l.
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | parallel (i)Most veins arranged parallel to the length of leaf, mostly no pronounced main vein (usually in elongate to linear leaves)
example: Most Monocotyledonae, Plantago, Veratrum, a lot of Caryophyllaceae looks like that. 
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants (i)Small, colourless or green flowers
example: Betula, grasslike plants: Carex, Setaria, Juncus
|
| Flower colour: (i)Attention: assess colour of the most colourful parts of the flower, but not of the stamens; be aware of single plants with a mutation (mostly white) on flower colour. | greenish (i)petals absent or not distinctly different from colours of leaves, only stigmas (white) or anthers (yellow) may differ in color
example: Chenopodium, Triglochin
|
| Perianth arrangement: (i)Attention: in some plants, flowers may be dimorphic in different ways (dioecious or gynodioecious). If flowers vary, record the characters of the most showy flowers. | simple, similar (i)Only one type of perianth leaves (tepals)
example: Tulipa 
|
| Diameter of flower: (i)Diameter of flower or flower head. | to 5 mm (i)
example: Aruncus
|
| Flower symmetry: (i)Symmetry of the perianth leaves. Attention: to assess this character, look on sepals, petals and stamens, but neglect carpels and ovary. | radiary, regular (actinomorphic) (i)More than two axis of symmetry
example: Saxifraga: 5; Iris: 3 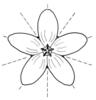
|
| Petal / Tepal number: (i)Number of petal leaves (inner perianth leaves, usually coloured). | 6 (i)
example: Allium, Lilium, Dactylorhiza
|
| Petal / Tepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the petal leaves connected? Petals sympetalous. | free (i)all petal leaves separate from each other
example: Anthriscus
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum
|
| Stamen number: (i)Attention: We ask for the reproductive organs of the flower dispersing pollen. Count only fully fertile stamens, not staminodia (e.g. Parnassia). | 6 (i)
example: Veratrum, Smelowskia, Juncus
|
| Stamen fusion: (i)To which degree are the stamens fused? Attention: Whereas the pollen sacs itself are often free., their stalks (filaments) may be fused. Here, we count them as fused if they are together over at least one thirth of their length. | free (i)Stamens with separate bases
example: Malus
|
| Pistil number: (i)Number of pistils (female floral organs: style, if developed; stigma and carpels/ovary together build the pistil). | 1 (i)One carpel, but clearly one stigma
example: Pyrola, Primula, Alyssum
|
| Carpel fusion: (i)To which degree are the carpels (modified leaf forming simple pistil or part of a compound pistil) fused. | fused (i)Carpels united into an ovary, only styles are free
example: Malus, Berberis
|
| Style number: (i)Portion of the pistil connecting the stigma to the ovary. | without (i)Without style, stigma sessile on the carpel
example: Acorus calamus
|
| Inflorescence (i)flowering part of a plant, describes the arrangement of the flowers on the flowering axis | |
| Inflorescence: (i)Structure of the inflorescence. | Flowers in inflorescence (i)No solitary flowers
Simple inflorescences (i)Flowers sessile on a main shoot or on short to long not branched side shoots
example: Polygonum bistorta  
|
| Appearance: (i)Outer look of the inflorescence. | terminal (i)Inflorescence is the highest point of the plant and may consist of a single flower only
example: Cypripedium, Rhaponticum, Ligularia sibirica, Echinops
|
| Hairs | |
| Has hairs?: | no hairs, glabrous
|
| Shoot/Stem (i)a young stem or branch | |
| Spines, thorns or prickles: (i)Shoot with conspicuous spines, thorns or prickles. | absent (i)Stem glabrous or hairy, but never with spines, thornes or prickles
example: Gentiana barbata
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | homorhizous (i)Many equal roots
example: Monocotyledonae  inherited by order Alismatales: homorhizous inherited by order Alismatales: homorhizous
|
| Runners: (i)Plant must be excavated; shoots, subterranean shoots connected by runners. | long root suckers or rhizomes (i)Plants grow new shoots from roots or subterranean shoots, called rhizomes, these spacing stems apart
example: Hippophae, Artemisia sericea
|
| Storage in below-ground structures: (i)Rhizomes or bulbs. | storage rhizomes (i)Horizontal, root like structures with scale leaves or their scars, these clearly thicker than the bases of above-ground shoots
example: Petasites, Iris
|