| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | | + - | Growth form (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | |  herb (i) Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody [example: Artemisia pectinata]  shrub, subshrub or semishrub (i) Shrub, multi-stemmed, mostly (0.2) 0.5 - 5 m high, shoots woody up to the tip [example: Caragana leucophloea]  tree (i) Woody plant with a clear main trunk, at least 2-3 m tall [example: Ulmus pumila] |
| Special growth forms or habits character not available for digital key |
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | | + - | Shape of blade (i)Easy for simple leaves. In compound leaves use the general shape of leaflet. Always check the ground for largest leaves of a plant. To be worked out: how to handle pinnate leaves? | | 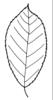 elliptic (including ovate and obovate) (i) Elliptic: broadest at the middle and narrower at the two equal ends; ovate: egg-shaped, attached at the broad end; obovate: attached at the narrower end [example: Limosella aquatica]  lanceolate (i) Lance-shaped; much longer than wide, with the widest point in the middle or below 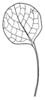 round to orbicular (i) Leaf at least as broad as long [example: Pyrola rotundifolia, Caltha] 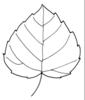 cordate (i) Heart shaped [example: Cortusa] 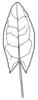 sagittate (i) Arrow-shaped [example: Rumex]  linear incl.grasslike or oblong (i) Leaves more than two times longer than broad with more or less parallel margins; see character: stipule for ligula [example: Dracocephalum ruyschiana, Poaceae, Scutellaria scordifolia, Pinus]  filiform (i) Leaves thread-like, at least more than ten times longer than broad [example: Potamogeton pectinatus, P. filiformis] 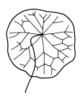 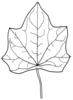 peltate (i) Leaf with with petiole attached to the lower surface of the blade [example: Menispermum dauricum]  scales (i) Short, broad and more or less adjacent to axis [example: Hypopitys, Orobanche, Ephedra] heterophyllous (i) Different kind of leaves on the same plant [example: Sagittaria, Ranunculus aquaticus]  |
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | | + - | Flower appearance and pollination (i)General appearance of the flower. | | not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants (i) Small, colourless or green flowers [example: Betula, grasslike plants: Carex, Setaria, Juncus] attractive, animal-pollinated (i) attractive and coloured flowers, mostly large, attracting surely animals [example: Trollius, Rosa, Chamaerhodos] |
| + - | Flower form (i)common forms of flowers ? Veronica | |  simple (flat) - Do not confuse with inflorescences as in some Asteraceae (i) Petals spread out, flower appearing flat [example: Mollugo, Trientalis, Pulsatilla, Saxifraga]  tubular to funnel-shaped (i) Petals form a tube, are often partially united to a cylindrical corolla, often surrounded by a calyx 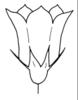 campanulate (i) Petals united to a bell-shaped corolla  bilabiate (i) Petals froming two lips, flower usually zygomorphic [example: Lamiaceae, Scrophulariaceae p.p.] 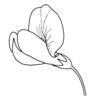   papilionaceous (i) Butterfly-like flower is structured: standard, 2 wings and keel [example: Most Fabaceae (Astragalus), Polygala] Hypanthium developed (i) Cup-shaped extension of the floral axis developed (receptacle accrescent) [example: Saxifragaceae, Rosaceae p.p., Lythraceae] |
|
Show