| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Rosaceae |
| Editor | S. Starke & S. Rilke, 2013 |
| Name acc. to: | APG II |
| Herbar: | list records    |
| Description: | Trees, shrubs, or herbs. Leaves mostly with paired stipules, blade often serrate at margin, rarely entire. Inflorescences various. Flowers usually actinomorphic, bisexual, rarely unisexual and then plants dioecious; with hypanthium (cup shaped extension of the floral axis); sepals usually 5, rarely fewer or more, sometimes with epicalyx segments, petals 5, sometimes absent; stamens usually numerous, rarely few, carpels 1 to many, ovary inferior, semi-inferior, or superior. Fruit a follicle, pome, nut or drupe, rarely a capsule, naked or enclosed in persistent hypanthium and sometimes also by sepals. |
| Confuse with: | Ranunculaceae |
| Comments: | Valued for fruits and for many horticultural ornamentals, bushes and trees. |
| Link to Flora of China: | http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=10776 |
| open map in a new window |  |
| genus: 28 |
| species: 145 |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf development: (i)Structure and development of leaves. | with green leaves (i)Plant with green leaves
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | attractive, animal-pollinated (i)attractive and coloured flowers, mostly large, attracting surely animals
example: Trollius, Rosa, Chamaerhodos
|
| Flower symmetry: (i)Symmetry of the perianth leaves. Attention: to assess this character, look on sepals, petals and stamens, but neglect carpels and ovary. | radiary, regular (actinomorphic) (i)More than two axis of symmetry
example: Saxifraga: 5; Iris: 3 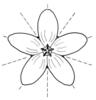
|
| Flower form: (i)common forms of flowers ? Veronica | simple (flat) - Do not confuse with inflorescences as in some Asteraceae (i)Petals spread out, flower appearing flat
example: Mollugo, Trientalis, Pulsatilla, Saxifraga 
|
| Petal / Tepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the petal leaves connected? Petals sympetalous. | free (i)all petal leaves separate from each other
example: Anthriscus
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum
|
| Stamen fusion: (i)To which degree are the stamens fused? Attention: Whereas the pollen sacs itself are often free., their stalks (filaments) may be fused. Here, we count them as fused if they are together over at least one thirth of their length. | free (i)Stamens with separate bases
example: Malus
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Rosales: allorhizous inherited by order Rosales: allorhizous
|