| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Bignoniaceae |
| Name acc. to: | APGII |
| Herbar: | list records  |
| open map in a new window | 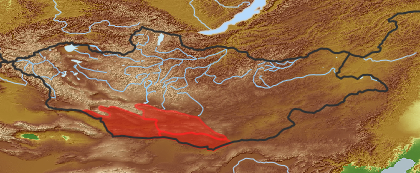 |
| genus: 1 |
| species: 1 |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita 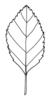  
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower symmetry: (i)Symmetry of the perianth leaves. Attention: to assess this character, look on sepals, petals and stamens, but neglect carpels and ovary. | zygomorphic (i)One axis of symmetry, monosymmetrical flowers
example: Pedicularis, Nepeta, Viola   
|
| Petal / Tepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the petal leaves connected? Petals sympetalous. | fused (i)petal leaves united, only tips are free (gamopetalous, sympetalous)
example: Linnaea, Adenophora, Stellera
|
| Ovary position: (i)For entirely or partly fused carpels, describe their position in relation to the insertion point of perianth leaves (best done by doing a longitudinal section of a flower). | superior (hypogynous) (i)Base of carpels attached above insertion point of perianth leaves, carpels free or fused
example: Delphinium, Anemone  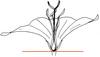
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Lamiales: allorhizous inherited by order Lamiales: allorhizous
|