| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Ranunculales |
| Family: | Hypecoaceae |
| Editor | S. Rilke, July 2009 |
| Name acc. to: | APweb |
| Herbar: | list records    |
| Synonym: | Paveraceae (p.p.) (acc. to Grubov 1982) |
| Description: | The Family is separated from Papaveraceae by 2-merous flowers and is closely related to Fumariaceae. |
| Tax. Comments: | Often included in Papaverceae. Hypecoum ist listed as Fumarioideae by Heywood (2007). |
| open map in a new window |  |
| genus: 1 |
| species: 2 |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | herb (i)Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody
example: Artemisia pectinata 
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | terrestrial (i)Plant grows on dry land
example: Orostachys spinosa
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita 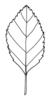  
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Ovary position: (i)For entirely or partly fused carpels, describe their position in relation to the insertion point of perianth leaves (best done by doing a longitudinal section of a flower). | superior (hypogynous) (i)Base of carpels attached above insertion point of perianth leaves, carpels free or fused
example: Delphinium, Anemone  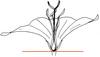  inherited by order Ranunculales: superior (hypogynous) inherited by order Ranunculales: superior (hypogynous)
|
| Fruit (i)the seed bearing organ, with or without adnate parts; a ripened ovary and any other structures which are attached and ripen with it. Aggregate fruits are handled like simple fruits for determination. | |
| Type of fruit: (i)Common fruit types (including pseudocarp). | Solitary fruits (i)  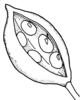 
Dehiscent fruits (i)Fruits open along a longitudinale line (except silicula)
silique (i)Dry fruit, opening with two valves and a separating wall inbetween
example: Brassicaceae, Hypecoum 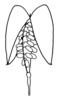 
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Ranunculales: allorhizous inherited by order Ranunculales: allorhizous
|