| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Alismatales |
| Family: | Zannichelliaceae |
| Genus: | Zannichellia |
| Scientific name: | Zannichellia palustris L. |
| Name acc. to: | Gubanov 1996, not in Grubov 1982/2001 |
| Herbar: | list records    |
| Synonym: | Z. pedunculata auct. Mong. (acc. to Grubov (1982)) |
| Description: | Stem filiform, intensely branched. Leaves narrow-linear 1.5-3.5 mm long. Fruits including pedicel 3-4 mm long, style shorter than fruit. |
| Tax. Comments: | All specimens examined have fruits about 3(4) mm long including 1-1.5 mm long style. The length is measured including pedicel. The style is mostly at least half as long as the seed bearing fruit part. Therefore all have been determined as Z. palustris s.l. Further studies are necessary to clear the taxonomic situation. |
| Link to Flora of China: | http://www.efloras.org/browse.aspx?flora_id=2&name_str=Zannichellia+palustris |
| open map in a new window | 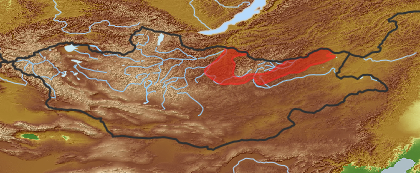 |
| Habitat: | In rivers, dirches, lakes (Flora of Siberia, Vol. 1, 2000). |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | herb (i)Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody
example: Artemisia pectinata   inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: herb inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: herb
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus  inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: no parasite/saprophyte inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: no parasite/saprophyte
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | water or swamp plant  inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: water or swamp plant inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: water or swamp plant
aquatic, submerged (i)Completely submerged water plant, onlys flowers may appear at the surface
example: Zannichellia  inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: aquatic, submerged inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: aquatic, submerged
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Shape of blade: (i)Easy for simple leaves. In compound leaves use the general shape of leaflet. Always check the ground for largest leaves of a plant. To be worked out: how to handle pinnate leaves? | filiform (i)Leaves thread-like, at least more than ten times longer than broad
example: Potamogeton pectinatus, P. filiformis   inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: filiform inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: filiform
|
| Leaf margin: (i)Structure of leaf margin (or that of a leaflet in case of compound leaves). Attention: Here we ask for the leaf margin, defined as all those dissections that separate the leaf for less than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. To be worked out: how to handle margin of pinnate leaves? | entire (i)Plain margin, not toothed
example: Iris   inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: entire inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: entire
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | parallel (i)Most veins arranged parallel to the length of leaf, mostly no pronounced main vein (usually in elongate to linear leaves)
example: Most Monocotyledonae, Plantago, Veratrum, a lot of Caryophyllaceae looks like that.   inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: parallel inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: parallel
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants (i)Small, colourless or green flowers
example: Betula, grasslike plants: Carex, Setaria, Juncus  inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants
|
| Perianth arrangement: (i)Attention: in some plants, flowers may be dimorphic in different ways (dioecious or gynodioecious). If flowers vary, record the characters of the most showy flowers. | absent or strongly reduced (i)No perianth leaves ensheathing stamen and/or carpels
example: Callitriche   inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: absent or strongly reduced inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: absent or strongly reduced
simple, similar (i)Only one type of perianth leaves (tepals)
example: Tulipa   inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: simple, similar inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: simple, similar
|
| Diameter of flower: (i)Diameter of flower or flower head. | from 5 mm to 10 mm (i)
example: Stellaria  inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: inherited by family Zannichelliaceae:
|
| Petal / Tepal number: (i)Number of petal leaves (inner perianth leaves, usually coloured). | none or reduced (i)But green sepals may exist
example: Thalictrum  inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: none or reduced inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: none or reduced
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum  inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: no spur inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: no spur
|
| Ovary position: (i)For entirely or partly fused carpels, describe their position in relation to the insertion point of perianth leaves (best done by doing a longitudinal section of a flower). | superior (hypogynous) (i)Base of carpels attached above insertion point of perianth leaves, carpels free or fused
example: Delphinium, Anemone    inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: superior (hypogynous) inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: superior (hypogynous)
|
| Inflorescence (i)flowering part of a plant, describes the arrangement of the flowers on the flowering axis | |
| Inflorescence: (i)Structure of the inflorescence. | Solitary flowers (i)Each flower grows on an own leafy stem there may be more than one, if the plant has many leafy shoots
example: Viola, Saxifraga hirculus, Rubus arcticus  inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: Solitary flowers inherited by family Zannichelliaceae: Solitary flowers
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | homorhizous (i)Many equal roots
example: Monocotyledonae  inherited by order Alismatales: homorhizous inherited by order Alismatales: homorhizous
|
| Distribution (i)region where the plant is likely to be found | |
| Distribution (Veg. Zones): (i)acc. to Grubov 1952 | Mongol-Daurian (i)In distribution data often named as '4' 
acc. to: Gubanov 1996 |