| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Dipsacales |
| Family: | Caprifoliaceae |
| Genus: | Lonicera |
| Scientific name: | Lonicera altaica Pall. ex DC. |
| Name acc. to: | Gubanov 1996 |
| Herbar: | list records    |
| Synonym: | L. caerulea L. var. altaica Pallas (acc. to Flora of Cina online) |
| Synonym: | L. caerulea L. ssp. altaica (Pallas) Gladkova (acc. to Flora of Siberia, Vol. 12 (2007)) |
| Description: | Shrub 0.3-1 (1.5) m tall. Young branches pilose. Leaves elliptical, 2-7 cm long, obtuse or +/- acuminate. Corolla slightly zygomorphic, 10-15 (18) mm long, yellowish. Fruits blue, looks like solitary (pseudocarp). |
| Comments: | See also: http://www.manfred-vesper.de/datei.php?did=244 |
| Link to Flora of China: | http://www.efloras.org/browse.aspx?flora_id=2&name_str=Lonicera+caerulea |
| open map in a new window | 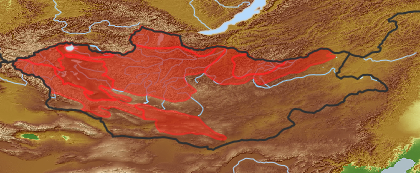 |
| Habitat: | Larch and cedarpine-larch forests and their fringes, cliffs, stone fields and screes, shrubberies in forest belt and lower part of alpine belt (Grubov 2001). |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | shrub, subshrub or semishrub (i)Shrub, multi-stemmed, mostly (0.2) 0.5 - 5 m high, shoots woody up to the tip
example: Caragana leucophloea   inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: shrub, subshrub or semishrub inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: shrub, subshrub or semishrub
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus  inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: no parasite/saprophyte inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: no parasite/saprophyte
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | terrestrial (i)Plant grows on dry land
example: Orostachys spinosa  inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: terrestrial inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: terrestrial
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf arrangement: (i)Arrangement of leaves at the stem. | opposite, opposite-decussate (i)Two leaves per node
example: Lamiaceae, e.g. Phlomis    inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: opposite, opposite-decussate inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: opposite, opposite-decussate
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita     inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: pinnate inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: pinnate
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Perianth arrangement: (i)Attention: in some plants, flowers may be dimorphic in different ways (dioecious or gynodioecious). If flowers vary, record the characters of the most showy flowers. | double, different (i)Two types of perianth leaves, differently coloured (sepals: outer periant leaves, usually greenish, and petals: inner perianth leaves, usually coloured)
example: Parnassia    inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: double, different inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: double, different
|
| Flower form: (i)common forms of flowers ? Veronica | bilabiate (i)Petals froming two lips, flower usually zygomorphic
example: Lamiaceae, Scrophulariaceae p.p.   inherited by genus Lonicera: bilabiate inherited by genus Lonicera: bilabiate
|
| Sepal number: (i)Number of sepal leaves (outer perianth leaves, calyx leaves, mostly greenish). Attention, this character applies only for flowers separated in sepals and petals, thus excluding most monocots. Be aware of the bracts (involucral leaves) of Asteraceae flowerheads, do not qualify these as sepals! Be also aware in Rosaceae is often an epicalyx developed, in this case count all parts. | 5 (i)
example: Polemonium  inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: 5 inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: 5
|
| Petal / Tepal number: (i)Number of petal leaves (inner perianth leaves, usually coloured). | 5 (i)
example: Potentilla  inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: 5 inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: 5
|
| Petal / Tepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the petal leaves connected? Petals sympetalous. | fused (i)petal leaves united, only tips are free (gamopetalous, sympetalous)
example: Linnaea, Adenophora, Stellera  inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: fused inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: fused
|
| Stamen number: (i)Attention: We ask for the reproductive organs of the flower dispersing pollen. Count only fully fertile stamens, not staminodia (e.g. Parnassia). | 4 (i)Extremely rare, may be absent
example: Plantago  inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: 4 inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: 4
5 (i)
example: Peucedanum  inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: 5 inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: 5
|
| Stamen fusion: (i)To which degree are the stamens fused? Attention: Whereas the pollen sacs itself are often free., their stalks (filaments) may be fused. Here, we count them as fused if they are together over at least one thirth of their length. | fused with a corolla (calyx in Thymelaeaceae) (i)Stamens with perianth leaves at least one third of the length of the filament
example: Orobanche, Salvia, Stellera  inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: fused with a corolla (calyx in Thymelaeaceae) inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: fused with a corolla (calyx in Thymelaeaceae)
|
| Ovary position: (i)For entirely or partly fused carpels, describe their position in relation to the insertion point of perianth leaves (best done by doing a longitudinal section of a flower). | intermediate ovary (i)Ovary partly or fully underneath the perianth leaves, ovary not fused with axis but surrounded by a flower cup
example: Prunus, a lot of Rosaceae  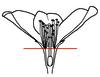  inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: intermediate ovary inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: intermediate ovary
inferior (i)Ovary below the point where perianth leaves are inserted, always fused to an ovary
example: Vaccinum  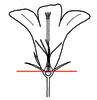  inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: inferior inherited by family Caprifoliaceae: inferior
|
| Hairs | |
| Has hairs?: | has hairs  inherited by genus Lonicera: has hairs inherited by genus Lonicera: has hairs
|
| Hairs: (i)Appearance, structure, coverage of hairs on plant. | on leaf (i)Hairs on upper side, lower side or on margin of leaf  inherited by genus Lonicera: on leaf inherited by genus Lonicera: on leaf
leaf upper side (i)Has hairs on leaves upper side (blade)  inherited by genus Lonicera: leaf upper side inherited by genus Lonicera: leaf upper side
appearance: soft (i)Hairs very flexible and soft, lay down at a touch
example: Lonicera xylosteum  inherited by genus Lonicera: appearance: soft inherited by genus Lonicera: appearance: soft
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Dipsacales: allorhizous inherited by order Dipsacales: allorhizous
|
| Distribution (i)region where the plant is likely to be found | |
| Distribution (Veg. Zones): (i)acc. to Grubov 1952 | Khubsgul (i)In distribution data often named as '1' 
Khentei (i)In distribution data often named as '2' 
Khangai (i)In distribution data often named as '3' 
Mongol-Daurian (i)In distribution data often named as '4' 
Khobdo (i)In distribution data often named as '6' 
Mongolian Altai (i)In distribution data often named as '7' 
Depression of Great Lakes (i)In distribution data often named as '10' 
Gobi-Altai (i)In distribution data often named as '13' 
acc. to: Gubanov 1996 |
| Distribution Khangay: (i)acc. Flora Khangaya 1989 | I
II
III
IV
V
|