| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Santalales |
| Family: | Santalaceae |
| Genus: | Thesium |
| Scientific name: | Thesium longifolium Turcz. ex Ledeb. |
| Name acc. to: | Gubanov 1996 |
| Herbar: | list records   |
| Link to Flora of China: | http://www.efloras.org/browse.aspx?flora_id=2&name_str=Thesium+longifolium |
| open map in a new window | 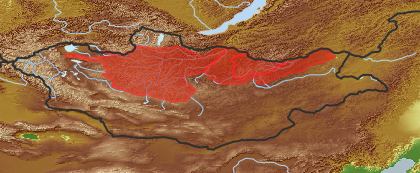 |
| Habitat: | Dry debris and soddy slopes, screes, fixed sands, shrubberies, dry forest fringes, river banks in forest and forest-steppe belts (Grubov 2001). |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | herb (i)Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody
example: Artemisia pectinata   inherited by genus Thesium: herb inherited by genus Thesium: herb
perennial (i)Living for several to many years, as opposed to annual and biennial  inherited by genus Thesium: perennial inherited by genus Thesium: perennial
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus  inherited by family Santalaceae: no parasite/saprophyte inherited by family Santalaceae: no parasite/saprophyte
Parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant not or not fully autonomous, leaves often without chlorophyll
example: Cuscuta, Corallorhiza, Epipogium (holomycotrophic)c  inherited by genus Thesium: Parasite/saprophyte inherited by genus Thesium: Parasite/saprophyte
semi-parasite (i)Plant with chlorophyll in green leaves, but roots suck on other plants
example: Melampyrum, Odontites, Pedicularis  inherited by genus Thesium: semi-parasite inherited by genus Thesium: semi-parasite
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | terrestrial (i)Plant grows on dry land
example: Orostachys spinosa  inherited by genus Thesium: terrestrial inherited by genus Thesium: terrestrial
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf development: (i)Structure and development of leaves. | with green leaves (i)Plant with green leaves  inherited by genus Thesium: with green leaves inherited by genus Thesium: with green leaves
|
| Leaf arrangement: (i)Arrangement of leaves at the stem. | alternate (i)One leaf per node; distiche: arranged in two vertical rows, equitant
example: Phragmites 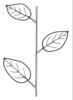   inherited by genus Thesium: alternate inherited by genus Thesium: alternate
|
| Simple or divided leaves: (i)Are the leaves simple or completely divided in several parts? Blade of the leaf entire or (more or less) deeply dissected. Attention: There are various appearances of the leaf margin (from entire to toothed and lobed). Here, we ignore this and ask only for dissections that separate the leaf for more than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. Sometimes, it is difficult to tell apart compound leaves from a shoot system with simple leaves: look for stipulae and/or axillary buds at the ground of the leaves: if only some possess these structures, the others are most likely leaflets of a compound leaf. | simple (i)Non-divided leaf, but margin may be incised nearly to the ground 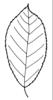  inherited by genus Thesium: simple inherited by genus Thesium: simple
|
| Leaf margin: (i)Structure of leaf margin (or that of a leaflet in case of compound leaves). Attention: Here we ask for the leaf margin, defined as all those dissections that separate the leaf for less than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. To be worked out: how to handle margin of pinnate leaves? | entire (i)Plain margin, not toothed
example: Iris 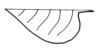  inherited by genus Thesium: entire inherited by genus Thesium: entire
|
| Petiole: (i)Leaf divided into stalk (petiole) and blade. | without (i)Leaves without petiole (stalk), sessile
example: Poaceae, Iris   inherited by genus Thesium: without inherited by genus Thesium: without
|
| Stipule: (i)Leaflets at the base of the petiole, these are smaller and of different shape. | none (i)Without stipules
example: Euphorbia, Ericaceae s.l.  inherited by genus Thesium: none inherited by genus Thesium: none
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita     inherited by family Santalaceae: pinnate inherited by family Santalaceae: pinnate
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants (i)Small, colourless or green flowers
example: Betula, grasslike plants: Carex, Setaria, Juncus  inherited by family Santalaceae: not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants inherited by family Santalaceae: not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants
attractive, animal-pollinated (i)attractive and coloured flowers, mostly large, attracting surely animals
example: Trollius, Rosa, Chamaerhodos  inherited by genus Thesium: attractive, animal-pollinated inherited by genus Thesium: attractive, animal-pollinated
|
| Perianth arrangement: (i)Attention: in some plants, flowers may be dimorphic in different ways (dioecious or gynodioecious). If flowers vary, record the characters of the most showy flowers. | simple, similar (i)Only one type of perianth leaves (tepals)
example: Tulipa   inherited by genus Thesium: simple, similar inherited by genus Thesium: simple, similar
|
| Diameter of flower: (i)Diameter of flower or flower head. | to 5 mm (i)
example: Aruncus  inherited by genus Thesium: inherited by genus Thesium:
|
| Flower symmetry: (i)Symmetry of the perianth leaves. Attention: to assess this character, look on sepals, petals and stamens, but neglect carpels and ovary. | radiary, regular (actinomorphic) (i)More than two axis of symmetry
example: Saxifraga: 5; Iris: 3   inherited by family Santalaceae: radiary, regular (actinomorphic) inherited by family Santalaceae: radiary, regular (actinomorphic)
|
| Flower form: (i)common forms of flowers ? Veronica | tubular to funnel-shaped (i)Petals form a tube, are often partially united to a cylindrical corolla, often surrounded by a calyx   inherited by genus Thesium: tubular to funnel-shaped inherited by genus Thesium: tubular to funnel-shaped
|
| Petal / Tepal number: (i)Number of petal leaves (inner perianth leaves, usually coloured). | 5 (i)
example: Potentilla  inherited by genus Thesium: 5 inherited by genus Thesium: 5
|
| Petal / Tepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the petal leaves connected? Petals sympetalous. | fused (i)petal leaves united, only tips are free (gamopetalous, sympetalous)
example: Linnaea, Adenophora, Stellera  inherited by genus Thesium: fused inherited by genus Thesium: fused
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum  inherited by genus Thesium: no spur inherited by genus Thesium: no spur
|
| Stamen number: (i)Attention: We ask for the reproductive organs of the flower dispersing pollen. Count only fully fertile stamens, not staminodia (e.g. Parnassia). | 5 (i)
example: Peucedanum  inherited by genus Thesium: 5 inherited by genus Thesium: 5
|
| Stamen fusion: (i)To which degree are the stamens fused? Attention: Whereas the pollen sacs itself are often free., their stalks (filaments) may be fused. Here, we count them as fused if they are together over at least one thirth of their length. | fused with a corolla (calyx in Thymelaeaceae) (i)Stamens with perianth leaves at least one third of the length of the filament
example: Orobanche, Salvia, Stellera  inherited by genus Thesium: fused with a corolla (calyx in Thymelaeaceae) inherited by genus Thesium: fused with a corolla (calyx in Thymelaeaceae)
|
| Pistil number: (i)Number of pistils (female floral organs: style, if developed; stigma and carpels/ovary together build the pistil). | 1 (i)One carpel, but clearly one stigma
example: Pyrola, Primula, Alyssum  inherited by genus Thesium: 1 inherited by genus Thesium: 1
|
| Carpel fusion: (i)To which degree are the carpels (modified leaf forming simple pistil or part of a compound pistil) fused. | fused (i)Carpels united into an ovary, only styles are free
example: Malus, Berberis  inherited by genus Thesium: fused inherited by genus Thesium: fused
|
| Style number: (i)Portion of the pistil connecting the stigma to the ovary. | 1  inherited by family Santalaceae: 1 inherited by family Santalaceae: 1
|
| Stigma number per style: (i)Number of stigmas per style. | 1 (i)One stigma, sessile or with a developed style  inherited by genus Thesium: 1 inherited by genus Thesium: 1
|
| Ovary position: (i)For entirely or partly fused carpels, describe their position in relation to the insertion point of perianth leaves (best done by doing a longitudinal section of a flower). | inferior (i)Ovary below the point where perianth leaves are inserted, always fused to an ovary
example: Vaccinum    inherited by family Santalaceae: inferior inherited by family Santalaceae: inferior
|
| Sex: (i)Distribution of male and female organs among flowers, only most commonly cases. | bisexual, hermaphrodite (i)All or nearly all flowers of a plant with male and female parts
example: Haplophyllum, Chenopodium  inherited by genus Thesium: bisexual, hermaphrodite inherited by genus Thesium: bisexual, hermaphrodite
|
| Fruit (i)the seed bearing organ, with or without adnate parts; a ripened ovary and any other structures which are attached and ripen with it. Aggregate fruits are handled like simple fruits for determination. | |
| Type of fruit: (i)Common fruit types (including pseudocarp). | Indehiscent fruits  inherited by genus Thesium: Indehiscent fruits inherited by genus Thesium: Indehiscent fruits
Solitary fruits (i)     inherited by genus Thesium: Solitary fruits inherited by genus Thesium: Solitary fruits
nut or nutlet (i)Dry fruit with a single, hard stone inside (and usually a large often edible embryo)   inherited by genus Thesium: nut or nutlet inherited by genus Thesium: nut or nutlet
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Santalales: allorhizous inherited by order Santalales: allorhizous
|
| Distribution (i)region where the plant is likely to be found | |
| Distribution (Veg. Zones): (i)acc. to Grubov 1952 | Khentei (i)In distribution data often named as '2' 
Khangai (i)In distribution data often named as '3' 
Mongol-Daurian (i)In distribution data often named as '4' 
acc. to: Gubanov 1996 |
| Distribution Khangay: (i)acc. Flora Khangaya 1989 | VI
|