| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Ceratophyllales |
| Family: | Ceratophyllaceae |
| Genus: | Ceratophyllum |
| Scientific name: | Ceratophyllum demersum L. |
| Name acc. to: | Gubanov 1996 |
| Herbar: | list records  |
| Description: | Submerged free-floating aquatic herb with slender stem strongly branched in upper part and whorls of finely divided linear leaves. Leaves filiform, 1-2 times dichotomously dissected into sparsely dentate lobes, whorled, 4-12 at a node. Flowers small, solitary, about 2 mm long. Fruit oval, smooth, 4-5 mm long, mostly with 3 long spines. |
| Comments: | Cosmopolitan species distinguished from other subaquatic plants by the whorled, bifid leaves. The species of genus Ceratophyllum are very variable and taxonomically difficult (Cook et al. 1974).
|
| Link to Flora of China: | http://www.efloras.org/browse.aspx?flora_id=2&name_str=Ceratophyllum+demersum |
| open map in a new window | 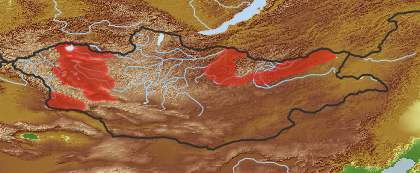 |
| Habitat: | Lakes, old river beds, river backwaters (Grubov 2001). |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | herb (i)Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody
example: Artemisia pectinata 
perennial (i)Living for several to many years, as opposed to annual and biennial
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus  inherited by family Ceratophyllaceae: no parasite/saprophyte inherited by family Ceratophyllaceae: no parasite/saprophyte
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | aquatic, submerged (i)Completely submerged water plant, onlys flowers may appear at the surface
example: Zannichellia  inherited by order Ceratophyllales: aquatic, submerged inherited by order Ceratophyllales: aquatic, submerged
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Simple or divided leaves: (i)Are the leaves simple or completely divided in several parts? Blade of the leaf entire or (more or less) deeply dissected. Attention: There are various appearances of the leaf margin (from entire to toothed and lobed). Here, we ignore this and ask only for dissections that separate the leaf for more than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. Sometimes, it is difficult to tell apart compound leaves from a shoot system with simple leaves: look for stipulae and/or axillary buds at the ground of the leaves: if only some possess these structures, the others are most likely leaflets of a compound leaf. | compound (i)Composed of several similar parts
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita     inherited by family Ceratophyllaceae: pinnate inherited by family Ceratophyllaceae: pinnate
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants (i)Small, colourless or green flowers
example: Betula, grasslike plants: Carex, Setaria, Juncus  inherited by family Ceratophyllaceae: not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants inherited by family Ceratophyllaceae: not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum  inherited by family Ceratophyllaceae: no spur inherited by family Ceratophyllaceae: no spur
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Ceratophyllales: allorhizous inherited by order Ceratophyllales: allorhizous
|
| Distribution (i)region where the plant is likely to be found | |
| Distribution (Veg. Zones): (i)acc. to Grubov 1952 | Mongol-Daurian (i)In distribution data often named as '4' 
Depression of Great Lakes (i)In distribution data often named as '10' 
Dzungarian Gobi (i)In distribution data often named as '14' 
|
| Distribution Khangay: (i)acc. Flora Khangaya 1989 | V
|