| Class: | gymnosperms |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae |
| Genus: | Juniperus |
| Scientific name: | Juniperus sabina L. |
| Name acc. to: | Gubanov 1996 |
| Herbar: | list records    |
| Comments: | see also: http://www.manfred-vesper.de/datei.php?did=230 |
| Link to Flora of China: | http://www.efloras.org/browse.aspx?flora_id=2&name_str=Juniperus+sabina |
| open map in a new window | 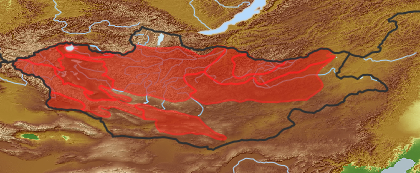 |
| Habitat: | Rocks, screes, stony places, stony bottom of small ravines and stream valleys, banks of brooks and streams in upper and montane-steppe belt and in lower part of high mountains (Grubov 2001). |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | shrub, subshrub or semishrub (i)Shrub, multi-stemmed, mostly (0.2) 0.5 - 5 m high, shoots woody up to the tip
example: Caragana leucophloea   inherited by family Cupressaceae: shrub, subshrub or semishrub inherited by family Cupressaceae: shrub, subshrub or semishrub
|
| Special growth forms or habits: | evergreen (i)Leaves remain on the plant in wintertime or in the dry season
example: Juniperus, Pinus, Ephedra  inherited by family Cupressaceae: evergreen inherited by family Cupressaceae: evergreen
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus  inherited by vasc. plants: no parasite/saprophyte inherited by vasc. plants: no parasite/saprophyte
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | terrestrial (i)Plant grows on dry land
example: Orostachys spinosa  inherited by vasc. plants: terrestrial inherited by vasc. plants: terrestrial
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf development: (i)Structure and development of leaves. | with green leaves (i)Plant with green leaves  inherited by vasc. plants: with green leaves inherited by vasc. plants: with green leaves  inherited by family Cupressaceae: with green leaves inherited by family Cupressaceae: with green leaves
needles or scales (i)Leaves short, broad more or less adjacent to axis (scales)) or acicular (needles)
example: Pinus (needles), Cupressus, Ephedra (scales)   inherited by vasc. plants: needles or scales inherited by vasc. plants: needles or scales
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Perianth arrangement: (i)Attention: in some plants, flowers may be dimorphic in different ways (dioecious or gynodioecious). If flowers vary, record the characters of the most showy flowers. | absent or strongly reduced (i)No perianth leaves ensheathing stamen and/or carpels
example: Callitriche   inherited by vasc. plants: absent or strongly reduced inherited by vasc. plants: absent or strongly reduced
|
| Ovary position: (i)For entirely or partly fused carpels, describe their position in relation to the insertion point of perianth leaves (best done by doing a longitudinal section of a flower). | absent (i)Without ovary: male flowers  inherited by order Pinales: absent inherited by order Pinales: absent
|
| Sex: (i)Distribution of male and female organs among flowers, only most commonly cases. | unisexual (i)
example: Rhodiola  inherited by vasc. plants: unisexual inherited by vasc. plants: unisexual  inherited by family Cupressaceae: unisexual inherited by family Cupressaceae: unisexual
monoecious (i)Male and female flowers at the same plant
example: Xanthium, Larix, Atriplex  inherited by family Cupressaceae: monoecious inherited by family Cupressaceae: monoecious
|
| Inflorescence (i)flowering part of a plant, describes the arrangement of the flowers on the flowering axis | |
| Inflorescence type: (i)Types of inflorescence. Attention: We here ask for the botanical nomenclature of inflorescences, which is sufficiently complicated. Tick only, if you are certain, or tick all inflorescence types that appear similar of these of the plant in question. | Cone (i)Flowers densely arranged along a short, often thickened axis, looking towards all sides
example: Pinus, Ephedra   inherited by vasc. plants: Cone inherited by vasc. plants: Cone
|
| Fruit (i)the seed bearing organ, with or without adnate parts; a ripened ovary and any other structures which are attached and ripen with it. Aggregate fruits are handled like simple fruits for determination. | |
| Type of fruit: (i)Common fruit types (including pseudocarp). | cone (i)No fruit, but often considered as fruit
example: Pinaceae, Cupressaceae, Ephedraceae   inherited by vasc. plants: cone inherited by vasc. plants: cone
Pseudofruit (i)Special types of diaspores, often no real fruits  inherited by vasc. plants: Pseudofruit inherited by vasc. plants: Pseudofruit
|
| Distribution (i)region where the plant is likely to be found | |
| Distribution (Veg. Zones): (i)acc. to Grubov 1952 | Khentei (i)In distribution data often named as '2' 
Khangai (i)In distribution data often named as '3' 
Mongol-Daurian (i)In distribution data often named as '4' 
Khobdo (i)In distribution data often named as '6' 
Mongolian Altai (i)In distribution data often named as '7' 
Middle Khalkha (i)In distribution data often named as '8' 
Depression of Great Lakes (i)In distribution data often named as '10' 
Gobi-Altai (i)In distribution data often named as '13' 
Dzungarian Gobi (i)In distribution data often named as '14' 
acc. to: Gubanov 1996 |
| Distribution Khangay: (i)acc. Flora Khangaya 1989 | I
II
III
IV
|
| Plant Status | |
| Red list status: (i)Rare Mongolian plants | very rare (Shiirevdamba 2007) (i)Very rare plant
|