| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Hippuridaceae |
| Genus: | Hippuris |
| Scientific name: | Hippuris vulgaris L. |
| Name acc. to: | Gubanov 1996 |
| Herbar: | list records    |
| Description: | Plant emergent. Stem simple straight 15-45 cm high, densely leaved. Leaves whorled, 8-16 leaves per verticil, leaves linear-lanceolate, entire, 1-4 cm long (submerged ones up to 8 cm), deflexed downward. Flowers bisexual or unisexual, very small, 1 per leaf axil. |
| Comments: | Genus generally accepted as monotypic, with only one very variable species but with ecological races. In Flora of China H. tetraphylla is differentiated on species level by leaf characters.
|
| Link to Flora of China: | http://www.efloras.org/browse.aspx?flora_id=2&name_str=Hippuris+vulgaris |
| open map in a new window | 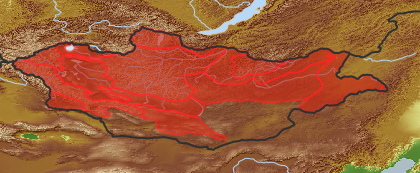 |
| Habitat: | Shallow waters of backwaters and old river beds, small and large lakes, alkaline bogs, springs and brooks (Grubov 2001). |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus  inherited by family Hippuridaceae: no parasite/saprophyte inherited by family Hippuridaceae: no parasite/saprophyte
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | water or swamp plant  inherited by family Hippuridaceae: water or swamp plant inherited by family Hippuridaceae: water or swamp plant
aquatic, submerged (i)Completely submerged water plant, onlys flowers may appear at the surface
example: Zannichellia  inherited by family Hippuridaceae: aquatic, submerged inherited by family Hippuridaceae: aquatic, submerged
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf arrangement: (i)Arrangement of leaves at the stem. | whorled or fascicled (i)Three or more leaves per node or leaves crowded.
example: Galium, Nitraria 
|
| Shape of blade: (i)Easy for simple leaves. In compound leaves use the general shape of leaflet. Always check the ground for largest leaves of a plant. To be worked out: how to handle pinnate leaves? | linear incl.grasslike or oblong (i)Leaves more than two times longer than broad with more or less parallel margins; see character: stipule for ligula
example: Dracocephalum ruyschiana, Poaceae, Scutellaria scordifolia, Pinus 
|
| Leaf margin: (i)Structure of leaf margin (or that of a leaflet in case of compound leaves). Attention: Here we ask for the leaf margin, defined as all those dissections that separate the leaf for less than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. To be worked out: how to handle margin of pinnate leaves? | entire (i)Plain margin, not toothed
example: Iris 
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita     inherited by family Hippuridaceae: pinnate inherited by family Hippuridaceae: pinnate
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants (i)Small, colourless or green flowers
example: Betula, grasslike plants: Carex, Setaria, Juncus  inherited by family Hippuridaceae: not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants inherited by family Hippuridaceae: not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum  inherited by family Hippuridaceae: no spur inherited by family Hippuridaceae: no spur
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Lamiales: allorhizous inherited by order Lamiales: allorhizous
|
| Distribution (i)region where the plant is likely to be found | |
| Distribution (Veg. Zones): (i)acc. to Grubov 1952 | Khubsgul (i)In distribution data often named as '1' 
Khentei (i)In distribution data often named as '2' 
Khangai (i)In distribution data often named as '3' 
Mongol-Daurian (i)In distribution data often named as '4' 
Great Khingan (i)In distribution data often named as '5' 
Khobdo (i)In distribution data often named as '6' 
Mongolian Altai (i)In distribution data often named as '7' 
Middle Khalkha (i)In distribution data often named as '8' 
East Mongolia (i)In distribution data often named as '9' 
Depression of Great Lakes (i)In distribution data often named as '10' 
Valley of Lakes (i)In distribution data often named as '11' 
Gobi-Altai (i)In distribution data often named as '13' 
Dzungarian Gobi (i)In distribution data often named as '14' 
|
| Distribution Khangay: (i)acc. Flora Khangaya 1989 | I
III
IV
V
|