| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Editor | S. Rilke, S. Starke, A. Weitkunat: Mai-November 2013; D. Podlech (Astragalus without fotos), Juli 2009-2011 |
| Name acc. to: | APGII |
| Herbar: | list records    |
| Synonym: | Papilionaceae; Leguminosae |
| Description: | Leaves simple, trifoliate or pinnate, sometimes terminating in a tendril. Flowers in racemes or heads. Butterfly flowers consist of banner (standard), two wings and a keel; only 2 petals are fused (postgenital), 10 stamens fused together (10) or 9 stamens fused and one stays free (9)+1. Fruit a pod (legume). |
| Comments: | One of the largest families of the world. Legumes fixes nitrogen with Rhizobium bacteria and enriches nutrient poor soils. |
| open map in a new window |  |
| genus: 26 |
| species: 324 |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf arrangement: (i)Arrangement of leaves at the stem. | alternate (i)One leaf per node; distiche: arranged in two vertical rows, equitant
example: Phragmites 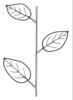 
|
| Stipule: (i)Leaflets at the base of the petiole, these are smaller and of different shape. | pair (i)A pair of free stipulae
example: Lathyrus, Trifolium 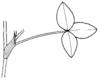
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita 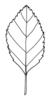  
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | attractive, animal-pollinated (i)attractive and coloured flowers, mostly large, attracting surely animals
example: Trollius, Rosa, Chamaerhodos
|
| Perianth arrangement: (i)Attention: in some plants, flowers may be dimorphic in different ways (dioecious or gynodioecious). If flowers vary, record the characters of the most showy flowers. | double, different (i)Two types of perianth leaves, differently coloured (sepals: outer periant leaves, usually greenish, and petals: inner perianth leaves, usually coloured)
example: Parnassia  
|
| Flower symmetry: (i)Symmetry of the perianth leaves. Attention: to assess this character, look on sepals, petals and stamens, but neglect carpels and ovary. | zygomorphic (i)One axis of symmetry, monosymmetrical flowers
example: Pedicularis, Nepeta, Viola   
|
| Flower form: (i)common forms of flowers ? Veronica | papilionaceous (i)Butterfly-like flower is structured: standard, 2 wings and keel
example: Most Fabaceae (Astragalus), Polygala   
|
| Sepal number: (i)Number of sepal leaves (outer perianth leaves, calyx leaves, mostly greenish). Attention, this character applies only for flowers separated in sepals and petals, thus excluding most monocots. Be aware of the bracts (involucral leaves) of Asteraceae flowerheads, do not qualify these as sepals! Be also aware in Rosaceae is often an epicalyx developed, in this case count all parts. | 5 (i)
example: Polemonium
|
| Sepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the sepal leaves connected? Attention, this character applies only for flowers separated in sepals and petals, thus excluding most monocots. Be aware of the bracts (involucral leaves) of Asteraceae flowerheads, do not qualify these as sepals! | fused (i)Leaves united, only tips are free
example: Fabaceae, Silene  
|
| Petal / Tepal number: (i)Number of petal leaves (inner perianth leaves, usually coloured). | 5 (i)
example: Potentilla
|
| Petal / Tepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the petal leaves connected? Petals sympetalous. | free (i)all petal leaves separate from each other
example: Anthriscus
fused (i)petal leaves united, only tips are free (gamopetalous, sympetalous)
example: Linnaea, Adenophora, Stellera
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum
|
| Stamen number: (i)Attention: We ask for the reproductive organs of the flower dispersing pollen. Count only fully fertile stamens, not staminodia (e.g. Parnassia). | 10 (i)
example: Silene
|
| Stamen fusion: (i)To which degree are the stamens fused? Attention: Whereas the pollen sacs itself are often free., their stalks (filaments) may be fused. Here, we count them as fused if they are together over at least one thirth of their length. | fused with each other (i)All or most stamens fused with each other to a tube-like structure
example: Caragana, Petasites
|
| Pistil number: (i)Number of pistils (female floral organs: style, if developed; stigma and carpels/ovary together build the pistil). | 1 (i)One carpel, but clearly one stigma
example: Pyrola, Primula, Alyssum
|
| Style number: (i)Portion of the pistil connecting the stigma to the ovary. | 1
|
| Stigma number per style: (i)Number of stigmas per style. | 1 (i)One stigma, sessile or with a developed style
|
| Ovary position: (i)For entirely or partly fused carpels, describe their position in relation to the insertion point of perianth leaves (best done by doing a longitudinal section of a flower). | superior (hypogynous) (i)Base of carpels attached above insertion point of perianth leaves, carpels free or fused
example: Delphinium, Anemone  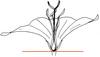
|
| Fruit (i)the seed bearing organ, with or without adnate parts; a ripened ovary and any other structures which are attached and ripen with it. Aggregate fruits are handled like simple fruits for determination. | |
| Type of fruit: (i)Common fruit types (including pseudocarp). | Solitary fruits (i)  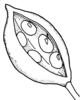 
Dehiscent fruits (i)Fruits open along a longitudinale line (except silicula)
legume (a special form of pod) (i)Dry to slightly fleshy fruit, formed of a single carpel, opening along one line only, without remaining wall
example: Fabaceae, Pea 
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Fabales: allorhizous inherited by order Fabales: allorhizous
|