| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Alismatales |
| Family: | Juncaginaceae |
| Editor | S. Rilke, June 2009 |
| Name acc. to: | APGII |
| Herbar: | list records    |
| Description: | Marsh glabrous herbs with basal, linear (semicylindrical), fleshy leaves and small, indistinct flowers in apical inflorescences. Perianth consists of glumceous tepals. |
| Comments: | The tepals in Triglochin are sometimes interpreted as extensions from the stamens. |
| open map in a new window |  |
| genus: 1 |
| species: 2 |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | herb (i)Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody
example: Artemisia pectinata 
|
| Size of plant: (i)Attention: use flowering or fruiting specimens to assess plant height (many biennial plants possess only a basal rosette in the first year). | from 100 mm to 250 mm
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | water or swamp plant
plants in swamps, marshes or bogs, leaves rising above water (i)Semiaquatic; plant terrestrial, but restricted to wet or moistured environments with ground water at or near the surface
example: Phragmites communis
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf arrangement: (i)Arrangement of leaves at the stem. | basal rosette (i)Leaves positioned at the base of the stem; stem often without leaves, no visible internodes (but flowers often on erect stems, and these may have few leaves)
example: Limonium, Potentilla, Plantago; also used in Liliales with basaly crouwded leaves (Tofieldia, Zigadenus etc.) 
|
| Simple or divided leaves: (i)Are the leaves simple or completely divided in several parts? Blade of the leaf entire or (more or less) deeply dissected. Attention: There are various appearances of the leaf margin (from entire to toothed and lobed). Here, we ignore this and ask only for dissections that separate the leaf for more than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. Sometimes, it is difficult to tell apart compound leaves from a shoot system with simple leaves: look for stipulae and/or axillary buds at the ground of the leaves: if only some possess these structures, the others are most likely leaflets of a compound leaf. | simple (i)Non-divided leaf, but margin may be incised nearly to the ground 
|
| Shape of blade: (i)Easy for simple leaves. In compound leaves use the general shape of leaflet. Always check the ground for largest leaves of a plant. To be worked out: how to handle pinnate leaves? | linear incl.grasslike or oblong (i)Leaves more than two times longer than broad with more or less parallel margins; see character: stipule for ligula
example: Dracocephalum ruyschiana, Poaceae, Scutellaria scordifolia, Pinus 
|
| Leaf margin: (i)Structure of leaf margin (or that of a leaflet in case of compound leaves). Attention: Here we ask for the leaf margin, defined as all those dissections that separate the leaf for less than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. To be worked out: how to handle margin of pinnate leaves? | entire (i)Plain margin, not toothed
example: Iris 
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | parallel (i)Most veins arranged parallel to the length of leaf, mostly no pronounced main vein (usually in elongate to linear leaves)
example: Most Monocotyledonae, Plantago, Veratrum, a lot of Caryophyllaceae looks like that. 
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | not attractive, wind-pollinated or some water plants (i)Small, colourless or green flowers
example: Betula, grasslike plants: Carex, Setaria, Juncus
|
| Flower colour: (i)Attention: assess colour of the most colourful parts of the flower, but not of the stamens; be aware of single plants with a mutation (mostly white) on flower colour. | greenish (i)petals absent or not distinctly different from colours of leaves, only stigmas (white) or anthers (yellow) may differ in color
example: Chenopodium, Triglochin
|
| Perianth arrangement: (i)Attention: in some plants, flowers may be dimorphic in different ways (dioecious or gynodioecious). If flowers vary, record the characters of the most showy flowers. | absent or strongly reduced (i)No perianth leaves ensheathing stamen and/or carpels
example: Callitriche 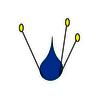
simple, similar (i)Only one type of perianth leaves (tepals)
example: Tulipa 
|
| Diameter of flower: (i)Diameter of flower or flower head. | from 5 mm to 10 mm (i)
example: Stellaria
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum
|
| Ovary position: (i)For entirely or partly fused carpels, describe their position in relation to the insertion point of perianth leaves (best done by doing a longitudinal section of a flower). | superior (hypogynous) (i)Base of carpels attached above insertion point of perianth leaves, carpels free or fused
example: Delphinium, Anemone  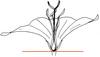
|
| Inflorescence (i)flowering part of a plant, describes the arrangement of the flowers on the flowering axis | |
| Inflorescence: (i)Structure of the inflorescence. | Flowers in inflorescence (i)No solitary flowers
Compound inflorescences (i)Flowers on shoots of higher orders (complex branched)
example: Solidago 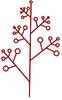
|
| Appearance: (i)Outer look of the inflorescence. | terminal (i)Inflorescence is the highest point of the plant and may consist of a single flower only
example: Cypripedium, Rhaponticum, Ligularia sibirica, Echinops
|
| Fruit (i)the seed bearing organ, with or without adnate parts; a ripened ovary and any other structures which are attached and ripen with it. Aggregate fruits are handled like simple fruits for determination. | |
| Seed number: (i)Estimate the number of seeds per fruit, if recognizable seeds are in the fruit (in rare cases a fruit may contain one seeded nuts: rose hip, carex). | 1 (i)A single seed (stone) or seed and fruit wall tightly connected
example: Prunus, Amygdalus: drupe
|
| Hairs | |
| Has hairs?: | no hairs, glabrous
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | homorhizous (i)Many equal roots
example: Monocotyledonae  inherited by order Alismatales: homorhizous inherited by order Alismatales: homorhizous
|