| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Lythraceae |
| Name acc. to: | APGII |
| Herbar: | list records  |
| Description: | Leaves opposite (on top sometimes alternate), simple, entire. Flowers bisexual, very small, with Hypanthium and epicalyx. |
| Tax. Comments: | One herbal species in Mongolia and about 31 genera with 650 species worldwide (widespread in tropical regions). |
| Link to Flora of China: | http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=10529 |
| open map in a new window | 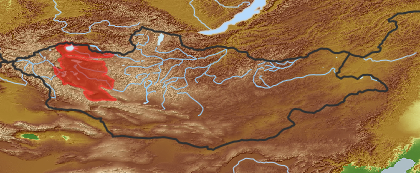 |
| genus: 1 |
| species: 1 |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf development: (i)Structure and development of leaves. | with green leaves (i)Plant with green leaves
|
| Simple or divided leaves: (i)Are the leaves simple or completely divided in several parts? Blade of the leaf entire or (more or less) deeply dissected. Attention: There are various appearances of the leaf margin (from entire to toothed and lobed). Here, we ignore this and ask only for dissections that separate the leaf for more than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. Sometimes, it is difficult to tell apart compound leaves from a shoot system with simple leaves: look for stipulae and/or axillary buds at the ground of the leaves: if only some possess these structures, the others are most likely leaflets of a compound leaf. | simple (i)Non-divided leaf, but margin may be incised nearly to the ground 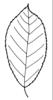
|
| Stipule: (i)Leaflets at the base of the petiole, these are smaller and of different shape. | none (i)Without stipules
example: Euphorbia, Ericaceae s.l.
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita   
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower symmetry: (i)Symmetry of the perianth leaves. Attention: to assess this character, look on sepals, petals and stamens, but neglect carpels and ovary. | radiary, regular (actinomorphic) (i)More than two axis of symmetry
example: Saxifraga: 5; Iris: 3 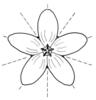
|
| Sex: (i)Distribution of male and female organs among flowers, only most commonly cases. | bisexual, hermaphrodite (i)All or nearly all flowers of a plant with male and female parts
example: Haplophyllum, Chenopodium
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Myrtales: allorhizous inherited by order Myrtales: allorhizous
|