| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Monotropaceae |
| Genus: | Hypopitys |
| open map in a new window |  |
| species: 1 |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | herb (i)Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody
example: Artemisia pectinata   inherited by family Monotropaceae: herb inherited by family Monotropaceae: herb
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | Full parasite/ saprophyte (i)Full parasites without chlorophyll, entire plant lacking green color, often succulent
example: Cistanche  inherited by family Monotropaceae: Full parasite/ saprophyte inherited by family Monotropaceae: Full parasite/ saprophyte
Parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant not or not fully autonomous, leaves often without chlorophyll
example: Cuscuta, Corallorhiza, Epipogium (holomycotrophic)c  inherited by family Monotropaceae: Parasite/saprophyte inherited by family Monotropaceae: Parasite/saprophyte
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | terrestrial (i)Plant grows on dry land
example: Orostachys spinosa  inherited by family Monotropaceae: terrestrial inherited by family Monotropaceae: terrestrial
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf development: (i)Structure and development of leaves. | without green leaves (i)Plant at flowering time (some geophytes) or over its whole life (many parasites) with reduced leaves without chlorophyll
example: Colchicum, Cuscuta, a lot of parasites  inherited by family Monotropaceae: without green leaves inherited by family Monotropaceae: without green leaves
|
| Length of leaves: (i)How long is the leaf, be carefull in compound leaves, measure the complete leaf. | from 6 mm to 10 mm  inherited by family Monotropaceae: inherited by family Monotropaceae:
|
| Petiole: (i)Leaf divided into stalk (petiole) and blade. | without (i)Leaves without petiole (stalk), sessile
example: Poaceae, Iris   inherited by family Monotropaceae: without inherited by family Monotropaceae: without
|
| Stipule: (i)Leaflets at the base of the petiole, these are smaller and of different shape. | none (i)Without stipules
example: Euphorbia, Ericaceae s.l.  inherited by family Monotropaceae: none inherited by family Monotropaceae: none
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower symmetry: (i)Symmetry of the perianth leaves. Attention: to assess this character, look on sepals, petals and stamens, but neglect carpels and ovary. | radiary, regular (actinomorphic) (i)More than two axis of symmetry
example: Saxifraga: 5; Iris: 3 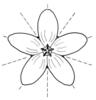  inherited by family Monotropaceae: radiary, regular (actinomorphic) inherited by family Monotropaceae: radiary, regular (actinomorphic)
|
| Inflorescence (i)flowering part of a plant, describes the arrangement of the flowers on the flowering axis | |
| Inflorescence: (i)Structure of the inflorescence. | Flowers in inflorescence (i)No solitary flowers  inherited by family Monotropaceae: Flowers in inflorescence inherited by family Monotropaceae: Flowers in inflorescence
|
| Appearance: (i)Outer look of the inflorescence. | terminal (i)Inflorescence is the highest point of the plant and may consist of a single flower only
example: Cypripedium, Rhaponticum, Ligularia sibirica, Echinops  inherited by family Monotropaceae: terminal inherited by family Monotropaceae: terminal
|
| Inflorescence type: (i)Types of inflorescence. Attention: We here ask for the botanical nomenclature of inflorescences, which is sufficiently complicated. Tick only, if you are certain, or tick all inflorescence types that appear similar of these of the plant in question. | raceme (i)Stalked flowers arranged along a simple main axis, often one by one in the axils of leaves, maturing from bottom upwards
example: Aconitum barbatum 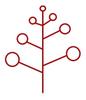  inherited by family Monotropaceae: raceme inherited by family Monotropaceae: raceme
|
| Fruit (i)the seed bearing organ, with or without adnate parts; a ripened ovary and any other structures which are attached and ripen with it. Aggregate fruits are handled like simple fruits for determination. | |
| Consistency: (i)Fleshy fruits or dry fruits, see dispersal adaptations for further classification. | dry (i)With a dry outer shell, no fleshy parts, but seed (embryo) could be edible  inherited by family Monotropaceae: dry inherited by family Monotropaceae: dry
|
| Type of fruit: (i)Common fruit types (including pseudocarp). | Solitary fruits (i)  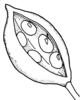   inherited by family Monotropaceae: Solitary fruits inherited by family Monotropaceae: Solitary fruits
capsule (i)Dry dehiscent fruit, releasing seeds by slits or holes.
example: Poppy, most Caryophyllaceae, Cerastium, a lot of Scrophulariaceae, Iris (oppened capsule looks like Delphinium), Zygophyllum - it is a very common fruit type 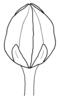  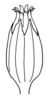  inherited by family Monotropaceae: capsule inherited by family Monotropaceae: capsule
Dehiscent fruits (i)Fruits open along a longitudinale line (except silicula)  inherited by family Monotropaceae: Dehiscent fruits inherited by family Monotropaceae: Dehiscent fruits
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Ericales: allorhizous inherited by order Ericales: allorhizous
|