| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Vicia |
| Scientific name: | Vicia amoena Fisch. |
| Name acc. to: | Gubanov 1996 |
| Herbar: | list records  |
| Description: | Perennial, 60-100 cm tall, climbing. Leaves 5-7 paired, leftlets oval to lanceolate, 2-4 cm long, 8-15 mm wide, leaf axis terminating in branched tendril. Flowers in racemes by (8)10-20, calyx teeth lanceolate-subulate; petals blue, 12-15 mm long; standard limb longer than unguis; keel much shorter than standard. |
| Confuse with: | V. multicaulis |
| Tax. Comments: | Differentiated from V. multicaulis by broader leaflets, more flowers per raceme, smaller flowers with keel shorter than standard. |
| Link to Flora of China: | http://www.efloras.org/browse.aspx?flora_id=2&name_str=Vicia+amoena |
| open map in a new window |  |
| Habitat: | Larch, pine and birch forests, meadows, shrubberies and foerst fringes, waterside meadows, river banks (Grubov 2001). |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | herb (i)Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody
example: Artemisia pectinata   inherited by genus Vicia: herb inherited by genus Vicia: herb
perennial (i)Living for several to many years, as opposed to annual and biennial
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus  inherited by family Fabaceae: no parasite/saprophyte inherited by family Fabaceae: no parasite/saprophyte
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | terrestrial (i)Plant grows on dry land
example: Orostachys spinosa  inherited by genus Vicia: terrestrial inherited by genus Vicia: terrestrial
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf arrangement: (i)Arrangement of leaves at the stem. | alternate (i)One leaf per node; distiche: arranged in two vertical rows, equitant
example: Phragmites    inherited by family Fabaceae: alternate inherited by family Fabaceae: alternate
|
| Simple or divided leaves: (i)Are the leaves simple or completely divided in several parts? Blade of the leaf entire or (more or less) deeply dissected. Attention: There are various appearances of the leaf margin (from entire to toothed and lobed). Here, we ignore this and ask only for dissections that separate the leaf for more than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. Sometimes, it is difficult to tell apart compound leaves from a shoot system with simple leaves: look for stipulae and/or axillary buds at the ground of the leaves: if only some possess these structures, the others are most likely leaflets of a compound leaf. | paripinnate / evenpinnate (i)A pinnate leaf with all leaflets in pairs  inherited by genus Vicia: paripinnate / evenpinnate inherited by genus Vicia: paripinnate / evenpinnate
compound (i)Composed of several similar parts  inherited by genus Vicia: compound inherited by genus Vicia: compound
pinnate (i)With leaflets on both sides of an axis, at least 2 pairs or more
example: Onobrychis   inherited by genus Vicia: pinnate inherited by genus Vicia: pinnate
bipinnate (i)Twofold pinnate (two levels of pinnae) 
|
| Shape of blade: (i)Easy for simple leaves. In compound leaves use the general shape of leaflet. Always check the ground for largest leaves of a plant. To be worked out: how to handle pinnate leaves? | lanceolate (i)Lance-shaped; much longer than wide, with the widest point in the middle or below 
|
| Leaf margin: (i)Structure of leaf margin (or that of a leaflet in case of compound leaves). Attention: Here we ask for the leaf margin, defined as all those dissections that separate the leaf for less than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. To be worked out: how to handle margin of pinnate leaves? | serrate / dentate / crenulate (i)Margin saw-like or rounded teethed
example: Betula, Lophanthus (crenulate) 
finely serrate / dentate (i)Fine teeth, more than 20 per leaf length; usually only one lateral vein per tooth
example: Pedicularis 
|
| Stipule: (i)Leaflets at the base of the petiole, these are smaller and of different shape. | pair (i)A pair of free stipulae
example: Lathyrus, Trifolium   inherited by family Fabaceae: pair inherited by family Fabaceae: pair
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita     inherited by family Fabaceae: pinnate inherited by family Fabaceae: pinnate
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | attractive, animal-pollinated (i)attractive and coloured flowers, mostly large, attracting surely animals
example: Trollius, Rosa, Chamaerhodos  inherited by family Fabaceae: attractive, animal-pollinated inherited by family Fabaceae: attractive, animal-pollinated
|
| Flower colour: (i)Attention: assess colour of the most colourful parts of the flower, but not of the stamens; be aware of single plants with a mutation (mostly white) on flower colour. | white (i)Most plants of the population white
example: Pleurospermum, Maianthemum  inherited by genus Vicia: white inherited by genus Vicia: white
pink (i)Between red and white
example: Centaurium
purple to violet (i)All colors between purple and violet, often changing with flower age
example: Pulmonaria  inherited by genus Vicia: purple to violet inherited by genus Vicia: purple to violet
blue (i)Bluish colours with mixture to red to deep blue
example: Myosotis, Dracocephalum  inherited by genus Vicia: blue inherited by genus Vicia: blue
|
| Perianth arrangement: (i)Attention: in some plants, flowers may be dimorphic in different ways (dioecious or gynodioecious). If flowers vary, record the characters of the most showy flowers. | double, different (i)Two types of perianth leaves, differently coloured (sepals: outer periant leaves, usually greenish, and petals: inner perianth leaves, usually coloured)
example: Parnassia    inherited by family Fabaceae: double, different inherited by family Fabaceae: double, different
|
| Flower symmetry: (i)Symmetry of the perianth leaves. Attention: to assess this character, look on sepals, petals and stamens, but neglect carpels and ovary. | zygomorphic (i)One axis of symmetry, monosymmetrical flowers
example: Pedicularis, Nepeta, Viola     inherited by family Fabaceae: zygomorphic inherited by family Fabaceae: zygomorphic
|
| Flower form: (i)common forms of flowers ? Veronica | papilionaceous (i)Butterfly-like flower is structured: standard, 2 wings and keel
example: Most Fabaceae (Astragalus), Polygala 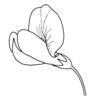    inherited by family Fabaceae: papilionaceous inherited by family Fabaceae: papilionaceous
|
| Sepal number: (i)Number of sepal leaves (outer perianth leaves, calyx leaves, mostly greenish). Attention, this character applies only for flowers separated in sepals and petals, thus excluding most monocots. Be aware of the bracts (involucral leaves) of Asteraceae flowerheads, do not qualify these as sepals! Be also aware in Rosaceae is often an epicalyx developed, in this case count all parts. | 5 (i)
example: Polemonium  inherited by family Fabaceae: 5 inherited by family Fabaceae: 5
|
| Sepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the sepal leaves connected? Attention, this character applies only for flowers separated in sepals and petals, thus excluding most monocots. Be aware of the bracts (involucral leaves) of Asteraceae flowerheads, do not qualify these as sepals! | fused (i)Leaves united, only tips are free
example: Fabaceae, Silene 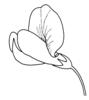   inherited by family Fabaceae: fused inherited by family Fabaceae: fused
|
| Petal / Tepal number: (i)Number of petal leaves (inner perianth leaves, usually coloured). | 5 (i)
example: Potentilla  inherited by family Fabaceae: 5 inherited by family Fabaceae: 5
|
| Petal / Tepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the petal leaves connected? Petals sympetalous. | free (i)all petal leaves separate from each other
example: Anthriscus  inherited by family Fabaceae: free inherited by family Fabaceae: free
fused (i)petal leaves united, only tips are free (gamopetalous, sympetalous)
example: Linnaea, Adenophora, Stellera  inherited by family Fabaceae: fused inherited by family Fabaceae: fused
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum  inherited by family Fabaceae: no spur inherited by family Fabaceae: no spur
|
| Stamen number: (i)Attention: We ask for the reproductive organs of the flower dispersing pollen. Count only fully fertile stamens, not staminodia (e.g. Parnassia). | 10 (i)
example: Silene  inherited by family Fabaceae: 10 inherited by family Fabaceae: 10
|
| Stamen fusion: (i)To which degree are the stamens fused? Attention: Whereas the pollen sacs itself are often free., their stalks (filaments) may be fused. Here, we count them as fused if they are together over at least one thirth of their length. | fused with each other (i)All or most stamens fused with each other to a tube-like structure
example: Caragana, Petasites  inherited by family Fabaceae: fused with each other inherited by family Fabaceae: fused with each other
|
| Pistil number: (i)Number of pistils (female floral organs: style, if developed; stigma and carpels/ovary together build the pistil). | 1 (i)One carpel, but clearly one stigma
example: Pyrola, Primula, Alyssum  inherited by family Fabaceae: 1 inherited by family Fabaceae: 1
|
| Style number: (i)Portion of the pistil connecting the stigma to the ovary. | 1  inherited by family Fabaceae: 1 inherited by family Fabaceae: 1
|
| Stigma number per style: (i)Number of stigmas per style. | 1 (i)One stigma, sessile or with a developed style  inherited by family Fabaceae: 1 inherited by family Fabaceae: 1
|
| Ovary position: (i)For entirely or partly fused carpels, describe their position in relation to the insertion point of perianth leaves (best done by doing a longitudinal section of a flower). | superior (hypogynous) (i)Base of carpels attached above insertion point of perianth leaves, carpels free or fused
example: Delphinium, Anemone    inherited by family Fabaceae: superior (hypogynous) inherited by family Fabaceae: superior (hypogynous)
|
| Inflorescence (i)flowering part of a plant, describes the arrangement of the flowers on the flowering axis | |
| Appearance: (i)Outer look of the inflorescence. | terminal (i)Inflorescence is the highest point of the plant and may consist of a single flower only
example: Cypripedium, Rhaponticum, Ligularia sibirica, Echinops
|
| Inflorescence type: (i)Types of inflorescence. Attention: We here ask for the botanical nomenclature of inflorescences, which is sufficiently complicated. Tick only, if you are certain, or tick all inflorescence types that appear similar of these of the plant in question. | spike (spadix) (i)All flowers sessile and crowded along a main axis, there may be several spikes on a shoot; sometimes axis thickened (spadix)
example: Plantago, Carex vesicaria, Vicia, Typha (spadix)    inherited by genus Vicia: spike (spadix) inherited by genus Vicia: spike (spadix)
raceme (i)Stalked flowers arranged along a simple main axis, often one by one in the axils of leaves, maturing from bottom upwards
example: Aconitum barbatum 
|
| Fruit (i)the seed bearing organ, with or without adnate parts; a ripened ovary and any other structures which are attached and ripen with it. Aggregate fruits are handled like simple fruits for determination. | |
| Type of fruit: (i)Common fruit types (including pseudocarp). | Solitary fruits (i)     inherited by family Fabaceae: Solitary fruits inherited by family Fabaceae: Solitary fruits
Dehiscent fruits (i)Fruits open along a longitudinale line (except silicula)  inherited by family Fabaceae: Dehiscent fruits inherited by family Fabaceae: Dehiscent fruits
legume (a special form of pod) (i)Dry to slightly fleshy fruit, formed of a single carpel, opening along one line only, without remaining wall
example: Fabaceae, Pea   inherited by family Fabaceae: legume (a special form of pod) inherited by family Fabaceae: legume (a special form of pod)
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Fabales: allorhizous inherited by order Fabales: allorhizous
|
| Distribution (i)region where the plant is likely to be found | |
| Distribution (Veg. Zones): (i)acc. to Grubov 1952 | Khubsgul (i)In distribution data often named as '1' 
Khentei (i)In distribution data often named as '2' 
Khangai (i)In distribution data often named as '3' 
Mongol-Daurian (i)In distribution data often named as '4' 
Great Khingan (i)In distribution data often named as '5' 
Mongolian Altai (i)In distribution data often named as '7' 
Middle Khalkha (i)In distribution data often named as '8' 
East Mongolia (i)In distribution data often named as '9' 
acc. to: Gubanov 1996 |
| Distribution Khangay: (i)acc. Flora Khangaya 1989 | I
IV
V
|
| Phenology (i)flowering and fruting period | |
| Flowering Period: (i)Period of the year the plant is flowering | July
|
| Fruiting Period: (i)Period of the year the plant is fruiting | August
|
| Plant Use | |
| General Use: | forage plant (i)This plant is known as forage plant (Johnson 2003)
|