| Class: | angiosperms |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Serratula |
| Scientific name: | Serratula coronata L. |
| Name acc. to: | Gubanov 1996 |
| Herbar: | list records   |
| Synonym: | Mastrucium pinnatifidum Cassini ex Candolle (acc. to FOC) |
| Synonym: | S. manshurica Kitagawa (acc. to FOC) |
| Link to Flora of China: | http://www.efloras.org/browse.aspx?flora_id=2&name_str=Serratula+coronata |
| open map in a new window | 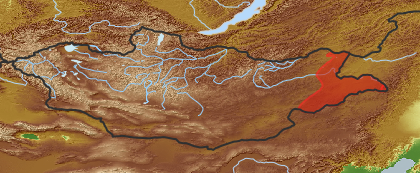 |
| Habitat: | Tall-grass meadows (Grubov 2001). |
| Habit (i)general appearance of a plant | |
| Growth form: (i)Herb, shrub, tree or climber. | herb (i)Herbaceous, erect plant, up to 2m high, mostly with a leafy shoot; if perennial, shoots die to the ground each season, shoots are not woody
example: Artemisia pectinata 
|
| Size of plant: (i)Attention: use flowering or fruiting specimens to assess plant height (many biennial plants possess only a basal rosette in the first year). | from 600 mm to 1000 mm
from 1000 mm to 3000 mm
|
| Parasite status: (i)Is the plant a half- or full parasite? | no parasite/saprophyte (i)Plant fully autonomous, leaves with chlorophyll
example: Most plants, Ranunculus  inherited by family Asteraceae: no parasite/saprophyte inherited by family Asteraceae: no parasite/saprophyte
|
| Water or terrestrial plant: (i)Where do the plants grow? | terrestrial (i)Plant grows on dry land
example: Orostachys spinosa  inherited by family Asteraceae: terrestrial inherited by family Asteraceae: terrestrial
|
| Leaf (i)expanded, usually photosynthetic organ of a plant (including phylloclades) | |
| Leaf development: (i)Structure and development of leaves. | with green leaves (i)Plant with green leaves  inherited by family Asteraceae: with green leaves inherited by family Asteraceae: with green leaves
|
| Leaf arrangement: (i)Arrangement of leaves at the stem. | alternate (i)One leaf per node; distiche: arranged in two vertical rows, equitant
example: Phragmites    inherited by genus Serratula: alternate inherited by genus Serratula: alternate
|
| Simple or divided leaves: (i)Are the leaves simple or completely divided in several parts? Blade of the leaf entire or (more or less) deeply dissected. Attention: There are various appearances of the leaf margin (from entire to toothed and lobed). Here, we ignore this and ask only for dissections that separate the leaf for more than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. Sometimes, it is difficult to tell apart compound leaves from a shoot system with simple leaves: look for stipulae and/or axillary buds at the ground of the leaves: if only some possess these structures, the others are most likely leaflets of a compound leaf. | simple (i)Non-divided leaf, but margin may be incised nearly to the ground 
pinnatisected, but simple leaf (i)Leaf divided to more than 1/3 of blade; there is a gradual transition from deeply divided leaves to pinnate leaves
example: Papaver 
|
| Shape of blade: (i)Easy for simple leaves. In compound leaves use the general shape of leaflet. Always check the ground for largest leaves of a plant. To be worked out: how to handle pinnate leaves? | elliptic (including ovate and obovate) (i)Elliptic: broadest at the middle and narrower at the two equal ends; ovate: egg-shaped, attached at the broad end; obovate: attached at the narrower end
example: Limosella aquatica 
|
| Length of leaves: (i)How long is the leaf, be carefull in compound leaves, measure the complete leaf. | more than 50 mm
|
| Width of leaves: (i)How broad is the leaf, be carefull in compound leaves, measure the complete leaf. | > 3 cm (i)6 arten prüfen
|
| Leaf margin: (i)Structure of leaf margin (or that of a leaflet in case of compound leaves). Attention: Here we ask for the leaf margin, defined as all those dissections that separate the leaf for less than one third of its length or width, whatever is smaller. To be worked out: how to handle margin of pinnate leaves? | serrate / dentate / crenulate (i)Margin saw-like or rounded teethed
example: Betula, Lophanthus (crenulate) 
|
| Petiole: (i)Leaf divided into stalk (petiole) and blade. | with (i)Leaves with petiole (stalk) 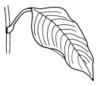
without (i)Leaves without petiole (stalk), sessile
example: Poaceae, Iris 
|
| Stipule: (i)Leaflets at the base of the petiole, these are smaller and of different shape. | none (i)Without stipules
example: Euphorbia, Ericaceae s.l.  inherited by family Asteraceae: none inherited by family Asteraceae: none
|
| Leaf colour upper side: (i)Shades of green on the leaf, upper side. | green (i)Clear green
example: Tribulus terrestris
|
| Leaf colour lower side: (i)Shades of green on the leaf, lower side. | green (i)Clear green, in most species
example: Angelica decurrens
|
| Leaf veination: (i)Arrangement of the main veins of a leaf. | pinnate (i)One main vein, several side veins, sometimes inconspicuous
example: Cicerbita 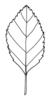    inherited by family Asteraceae: pinnate inherited by family Asteraceae: pinnate
|
| Flower (i)reproductive portion of the plant, consisting of sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils | |
| Flower appearance and pollination: (i)General appearance of the flower. | attractive, animal-pollinated (i)attractive and coloured flowers, mostly large, attracting surely animals
example: Trollius, Rosa, Chamaerhodos  inherited by family Asteraceae: attractive, animal-pollinated inherited by family Asteraceae: attractive, animal-pollinated
|
| Flower colour: (i)Attention: assess colour of the most colourful parts of the flower, but not of the stamens; be aware of single plants with a mutation (mostly white) on flower colour. | purple to violet (i)All colors between purple and violet, often changing with flower age
example: Pulmonaria
|
| Perianth arrangement: (i)Attention: in some plants, flowers may be dimorphic in different ways (dioecious or gynodioecious). If flowers vary, record the characters of the most showy flowers. | double, different (i)Two types of perianth leaves, differently coloured (sepals: outer periant leaves, usually greenish, and petals: inner perianth leaves, usually coloured)
example: Parnassia 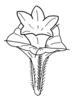   inherited by family Asteraceae: double, different inherited by family Asteraceae: double, different
|
| Diameter of flower: (i)Diameter of flower or flower head. | from 20 mm to 40 mm (i)
example: Aquilegia
|
| Flower symmetry: (i)Symmetry of the perianth leaves. Attention: to assess this character, look on sepals, petals and stamens, but neglect carpels and ovary. | radiary, regular (actinomorphic) (i)More than two axis of symmetry
example: Saxifraga: 5; Iris: 3 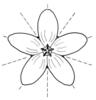  inherited by genus Serratula: radiary, regular (actinomorphic) inherited by genus Serratula: radiary, regular (actinomorphic)
|
| Petal / Tepal number: (i)Number of petal leaves (inner perianth leaves, usually coloured). | 5 (i)
example: Potentilla  inherited by family Asteraceae: 5 inherited by family Asteraceae: 5
|
| Petal / Tepal fusion: (i)To which degree are the petal leaves connected? Petals sympetalous. | fused (i)petal leaves united, only tips are free (gamopetalous, sympetalous)
example: Linnaea, Adenophora, Stellera  inherited by family Asteraceae: fused inherited by family Asteraceae: fused
|
| Spur: (i)A hollow, slender, sac-like appendage of the perianth leaves, storing nectar. | no spur (i)Flower without appendage
example: Peganum  inherited by family Asteraceae: no spur inherited by family Asteraceae: no spur
|
| Stamen number: (i)Attention: We ask for the reproductive organs of the flower dispersing pollen. Count only fully fertile stamens, not staminodia (e.g. Parnassia). | 5 (i)
example: Peucedanum  inherited by family Asteraceae: 5 inherited by family Asteraceae: 5
|
| Stamen fusion: (i)To which degree are the stamens fused? Attention: Whereas the pollen sacs itself are often free., their stalks (filaments) may be fused. Here, we count them as fused if they are together over at least one thirth of their length. | fused with each other (i)All or most stamens fused with each other to a tube-like structure
example: Caragana, Petasites  inherited by family Asteraceae: fused with each other inherited by family Asteraceae: fused with each other
|
| Pistil number: (i)Number of pistils (female floral organs: style, if developed; stigma and carpels/ovary together build the pistil). | 2 (i)Two stigmas, often cleaved like a snakes tongue
example: Salvia, Arnica, Bupleurum, Bromus, Saxifraga, Veronica  inherited by family Asteraceae: 2 inherited by family Asteraceae: 2
|
| Carpel number: (i)Number of carpels (carpel: forming a simple pistil or part of a compound pistil, modified leaf). | 2  inherited by family Asteraceae: 2 inherited by family Asteraceae: 2
|
| Carpel fusion: (i)To which degree are the carpels (modified leaf forming simple pistil or part of a compound pistil) fused. | fused (i)Carpels united into an ovary, only styles are free
example: Malus, Berberis  inherited by family Asteraceae: fused inherited by family Asteraceae: fused
|
| Style number: (i)Portion of the pistil connecting the stigma to the ovary. | 1  inherited by family Asteraceae: 1 inherited by family Asteraceae: 1
|
| Stigma number per style: (i)Number of stigmas per style. | 2 (i)Two stigmas, resulting from two fused carpels with or without developed style   inherited by family Asteraceae: 2 inherited by family Asteraceae: 2
|
| Ovary position: (i)For entirely or partly fused carpels, describe their position in relation to the insertion point of perianth leaves (best done by doing a longitudinal section of a flower). | inferior (i)Ovary below the point where perianth leaves are inserted, always fused to an ovary
example: Vaccinum  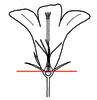  inherited by family Asteraceae: inferior inherited by family Asteraceae: inferior
|
| Sex: (i)Distribution of male and female organs among flowers, only most commonly cases. | bisexual, hermaphrodite (i)All or nearly all flowers of a plant with male and female parts
example: Haplophyllum, Chenopodium  inherited by genus Serratula: bisexual, hermaphrodite inherited by genus Serratula: bisexual, hermaphrodite
gynomonecious (i)Plant with hermaphrodite flowers, but beside this a significant proportion of flowers are purely male
example: Artemisia glauca
|
| Inflorescence (i)flowering part of a plant, describes the arrangement of the flowers on the flowering axis | |
| Inflorescence: (i)Structure of the inflorescence. | Flowers in inflorescence (i)No solitary flowers  inherited by family Asteraceae: Flowers in inflorescence inherited by family Asteraceae: Flowers in inflorescence
|
| Inflorescence type: (i)Types of inflorescence. Attention: We here ask for the botanical nomenclature of inflorescences, which is sufficiently complicated. Tick only, if you are certain, or tick all inflorescence types that appear similar of these of the plant in question. | head or capitulum (= calathidium) (i)Sessile flowers densely clustered on a compressed or widened axis, often surrounded by bracts, called involucral leaves
example: Asteraceae, Dipsacaceae, Sanguisorba, Trifolium  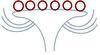  inherited by family Asteraceae: head or capitulum (= calathidium) inherited by family Asteraceae: head or capitulum (= calathidium)
|
| Fruit (i)the seed bearing organ, with or without adnate parts; a ripened ovary and any other structures which are attached and ripen with it. Aggregate fruits are handled like simple fruits for determination. | |
| Consistency: (i)Fleshy fruits or dry fruits, see dispersal adaptations for further classification. | dry (i)With a dry outer shell, no fleshy parts, but seed (embryo) could be edible  inherited by family Asteraceae: dry inherited by family Asteraceae: dry
|
| Type of fruit: (i)Common fruit types (including pseudocarp). | Indehiscent fruits  inherited by family Asteraceae: Indehiscent fruits inherited by family Asteraceae: Indehiscent fruits
achene (i)A small, dry, indehiscent fruit with a single seed
example: Asteraceae, Apiaceae (schizocarp), Dipsacaceae, Rosaceae, Ranunculaceae    inherited by family Asteraceae: achene inherited by family Asteraceae: achene
nut or nutlet (i)Dry fruit with a single, hard stone inside (and usually a large often edible embryo) 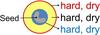  inherited by family Asteraceae: nut or nutlet inherited by family Asteraceae: nut or nutlet
|
| Opening of fruit: (i)Mode of dehiscence at maturity to release seeds. | not opening / indehiscent (i)Fruits remain closed at maturity and disperse with seeds inside
example: Corylus (nut), Vaccinium (berry)  inherited by family Asteraceae: not opening / indehiscent inherited by family Asteraceae: not opening / indehiscent
|
| Dispersal: (i)Appearance of fruit or seed (if single) and adaptations to dispersal. | Flying (wind dispersed) (i)Fruits or seeds with appendages to fly
example: Taraxacum, Atraphaxis, Pulsatilla  inherited by family Asteraceae: Flying (wind dispersed) inherited by family Asteraceae: Flying (wind dispersed)
|
| Seed number: (i)Estimate the number of seeds per fruit, if recognizable seeds are in the fruit (in rare cases a fruit may contain one seeded nuts: rose hip, carex). | 1 (i)A single seed (stone) or seed and fruit wall tightly connected
example: Prunus, Amygdalus: drupe  inherited by family Asteraceae: 1 inherited by family Asteraceae: 1
|
| Hairs | |
| Has hairs?: | no hairs, glabrous
has hairs
|
| Hairs: (i)Appearance, structure, coverage of hairs on plant. | on leaf (i)Hairs on upper side, lower side or on margin of leaf
coverage: scattered (i)Solitary hairs in large distances to each other
example: Dracocephalum origanoides
appearance: stiff (i)Hairs stiff but not pungent, erect
example: Myosotis
|
| Root / shoot below ground (i)plant part below ground (in most cases), including below ground shoots, without leaves | |
| Root type: (i)Organisation of the roots. | allorhizous (i)Plant with a conspicuous tap root, one larger tap root with side roots
example: Dicotyledonae  inherited by order Asterales: allorhizous inherited by order Asterales: allorhizous
|
| Distribution (i)region where the plant is likely to be found | |
| Distribution (Veg. Zones): (i)acc. to Grubov 1952 | Great Khingan (i)In distribution data often named as '5' 
East Mongolia (i)In distribution data often named as '9' 
|